Sarai Anayansi Zárate Chávez
Universidad Anáhuac campus Oaxaca

Juan Pablo García Guzmán
Universidad Anáhuac Mexico campus Norte

Amin H. Karim MD
Institute of Academic Medicine, Houston, Texas
Weill Medical College of Cornell University.
What Is a Blood Clot?
A blood clot also referred to as a thrombus (plural: thrombi), intravascular clot, or coagulum is a gelatinous or semi-solid mass of coagulated blood that forms within the circulatory system. When such a clot develops in the deep venous system, most commonly in the lower limbs, it is termed deep vein thrombosis (DVT), although it can also occur in the upper extremities.
A major complication of DVT is embolization, in which one or more thrombi detach and travel through the venous circulation often originating in the legs, pelvis, or groin and reach the pulmonary arteries, leading to a pulmonary embolism (PE). This condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical intervention.
Thrombus Formation and Intracardiac Clot Dynamics
A thrombus also referred to as a clot, blood clot, embolus (when mobile), or
thromboembolus (when causing obstruction) is the result of a complex interaction between endothelial injury, abnormal blood flow (stasis or turbulence), and a hypercoagulable state, often summarized by Virchow’s triad.
In the setting of acute vascular injury, particularly in acute coronary syndrome
(ACS), clot formation begins with platelet adhesion to exposed subendothelial
proteins at sites of plaque rupture or erosion. Once adhered, platelets become
activated, change shape, and release a variety of pro-thrombotic substances
including thromboxane A2, ADP, and serotonin, promoting further platelet
activation and local vasoconstriction. The surface expression of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors increases, facilitating platelet aggregation through fibrinogen bridging. Concurrently, the coagulation cascade is triggered, leading to thrombin generation. Thrombin amplifies platelet activation and converts fibrinogen into fibrin, which stabilizes the growing thrombus. As fibrin is laid down, a stable platelet-fibrin thrombus forms, which may partially or completely obstruct the vessel. If embolized, fragments of the thrombus may lodge downstream, causing ischemia or infarction.
Intracardiac thrombi form under somewhat different circumstances, often related to blood stasis or structural heart disease. In the left ventricle, thrombi can arise after anterior myocardial infarction, especially with regional wall motion abnormalities such as apical akinesis or dyskinesis. In non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy, the risk is lower but still present, particularly when left ventricular ejection fraction is severely reduced.
The left atrium, particularly the left atrial appendage, is a common site for thrombus formation in patients with atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, or significant mitral valve disease. Even in sinus rhythm, atrial mechanical dysfunction—as in cardiac amyloidosis—can predispose to thrombus formation. On the right side of the heart, thrombi may form in cases of central venous catheters, intracardiac devices, severe right ventricular dysfunction, or
hypercoagulable states. Additionally, mechanical prosthetic valves, especially with inadequate anticoagulation, are a high-risk source of thrombus formation and systemic embolism. Paradoxical embolism can occur in the presence of a patent foramen ovale (PFO) or atrial septal defect (ASD), where venous thrombi bypass the pulmonary circulation and enter the systemic arterial system through a right-to-left intracardiac shunt.
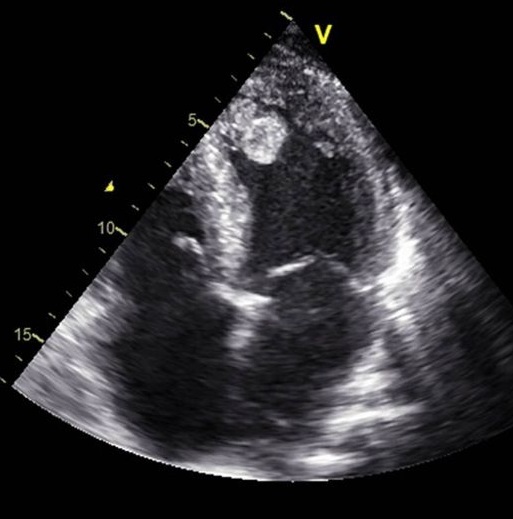
Diagnosis: Tests
The main diagnostic tests for detecting thrombi in the left ventricle are transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMRI) with delayed gadolinium enhancement. TTE is the most used initial technique due to its availability and low cost: however, its sensitivity is limited (approximately 21-35%), although its specificity is high (95-98%). The use of intravenous contrast agents in TTE improves sensitivity (up to 64%) without losing specificity. Transthoracic echocardiography has been utilized for identifying left ventricular thrombi since the early 1980s. In recent years, the introduction of echocardiographic contrast agents has improved detections accuracy, particularly in patients with suboptimal acoustic windows. TTE remains the initial diagnostic modality of choice for evaluating left ventricular thrombus. However, its limitations such as difficulty imaging patients with poor acoustic windows, can lead to considerable interobserver variability, potentially compromising diagnostic reliability. Cardiac magnetic resonance offers a diagnostic edge over echocardiography by allowing both myocardial tissue characterization and dynamic imaging. With recent advancements in imaging sequences and the use of paramagnetic contrast agents to enhance blood pool visualization, late gadolinium enhancement CMR may offer superior sensitivity for detecting left ventricular thrombi.
Recent epidemiologic tests have provided that the incidence of left ventricular
thrombus, using optimal imaging modalities, can reach up to 15% in patients with ST segment elevation myocardial infarction and up to 25% in those with anterior myocardial infarction. Although a standard transthoracic echocardiogram is frequently used for initial screening, its low sensitivity in detecting left ventricular thrombus requires the use of contrast (when not contraindicated) and/or cardiac MRI when there is a high pretest probability.
Transesophageal echocardiography does not provide advantages for visualizing
the ventricular apex and is not recommended as a second-line method for
ventricular thrombi.
The first study that was able to compare the diagnostic accuracies of CMRI,
contrast TTE and noncontrast TTE was performed by Weinsaft et al. That
demonstrated that even with administration of echocardiographic contrast agents, CMRI was still considerably more accurate modality in terms of thrombus detection.
CMR with late gadolinium enhancement is the gold standard, with a sensitivity of 82-88% and specificity of 99-100%, as it allows differentiation of the thrombus (avascular without enhancement) from the surrounding myocardium. It is especially recommended when TTE (even with contrast) is not diagnostic or clinical suspicion persists. Cardiac computed tomography can incidentally detect thrombi, but it is not validated for this purpose
Precise detection of left ventricular thrombi is crucial, as it frequently guides the initiation of anticoagulation therapy to reduce the risk of embolic complications. While current guidelines suggest that starting anticoagulation may be reasonable in patients with strong suspicion of thrombus such as those with apical akinesis or dyskinesis even without visible thrombus, selecting the most appropriate imaging modality is essential to ensure timely and evidence-based therapeutic decisions.
Complications
The main complications of thrombi in the left ventricle are systemic embolic events, especially ischemic stroke and peripheral arterial embolisms. Embolization occurs because the thrombus can detach and migrate into systemic circulation, affecting organs such as the brain, kidneys, spleen, or extremities. The risk of embolization is particularly high in the first few weeks after an acute myocardial infarction and can reach up to 22% depending on the morphology and follow up of the thrombus.
The incidence of systemic embolic events in patients with left ventricular thrombi varies depending on the population and clinical context. In patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), the incidence of left ventricular thrombus is 3.5% to 7.1% after previous AMI when cardiac magnetic resonance imaging is used, and the incidence of systemic embolism (including stroke) in the presence of thrombus is between 7% and 16% in the first few years after the event, with an annualized risk of 3.7% compared to 0.8% in patients without left ventricular thrombus. Other relevant complications include major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), which include death, reinfarction, and hospitalization for heart failure. The presence of left ventricular thrombus is associated with a significant increase in mortality and long-term adverse cardiovascular events. In addition, patients with persistent thrombus are at increased risk of bleeding, especially if they require prolonged anticoagulation.
The American Heart Association emphasizes that complete thrombus resolution is associated with lower mortality, while thrombus persistence, especially if mural and organized, carries a lower but not zero risk of embolization. The patient groups with the highest incidence of complications associated with thrombi in the left ventricle are mainly those with extensive acute myocardial infarction (AMI), especially anterior AMI, patients with ventricular aneurysm, and those with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). In addition, patients with dilated cardiomyopathy, either ischemic or non-ischemic, particularly those with severe systolic dysfunction, also have an elevated risk of embolic complications and major cardiovascular events.
In the context of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy, patients with dilated
cardiomyopathy show an even higher risk of systemic embolism compared to other non-ischemic etiologies and ischemic heart disease. The presence of mobile or protruding thrombi increases the risk of embolization, while thrombus persistence is associated with higher mortality and adverse events.
The American Heart Association points out that the combination of anterior AMI, low LVEF, ventricular aneurysm, and delayed reperfusion are factors that identify patients at higher risk of embolic complications and mortality associated with thrombi in the left ventricle.
The factors that increase the risk of thrombus formation in the left ventricle vary depending on the patient group, but they share pathophysiological mechanisms based on Virchow’s triad: ventricular dysfunction (stasis), endocardial damage, and inflammation/hypercoagulability. In patients with extensive acute myocardial infarction (AMI), especially anterior AMI, the highest risk factors are anterior location of the infarction, presence of ventricular aneurysm, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <30-40%, larger infarction size (elevated troponins), delayed reperfusion, and suboptimal coronary flow after intervention. The combination of reduced LVEF and segmental dysfunction (particularly apical) is the main predictor of thrombus and embolic complications or major cardiovascular events in all these groups. Systemic inflammation (elevated CRP) and the use of certain antithrombotic drugs may also contribute
Managment
Management of left Heart Thrombi (RHT)
The cornrstone of managment for intracardiac thrombus, particularly left ventricular thrombus, is therapeutic anticoagulantion. This strategy aims to reduce the risk of systemic embolism and promote trhombus resolution. Anticoagulation should be initiated promptly upon diagnosis, typically with intravenous unfractionated heparin, low molecular weight heparin, or a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC). Transition to oral therapy with either warfarin or a DOAC is the recommended available evidence suggests that anticoagulation significantly lowers embolic risk and increases the likelihood of thrombus resolution compared to no or subtherapeutic treatment. In particular, a higher time in therapeutic range with warfarin is associated with superior outcomes and appears to outweigh the bleeding risks, even in the presence of concurrent antiplatelet therapy. The standard duration of anticoagulation is a minimum of three months.
Follow-up
cardiac imaging, ideally using the same modality employed at diagnosis, should be performed at that point to assess thrombus resolution. If the thrombus persists without notable change, anticoagulation should be continued with periodic reassessment. In cases where the thrombus has decreased in size or displays features consistent with chronicity and reduced embolic potential, the decision to continue therapy should be based on ongoing embolic risk, such as persistent left ventricular dysfunction, aneurysm formation, or spontaneous echocardiographic contrast. If both the thrombus and contributing risk factors have resolved, evidenced by normalization of systolic function and absence of additional indications for anticoagulation, discontinuation of therapy may be appropriate. For patients who develop LVT in the context of prior MI (≥3 months) or chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy, no randomized controlled data exist to guide treatment duration. Nonetheless, anticoagulation for a period of 3 to 6 months is generally recommended. Beyond that, extended or indefinite therapy should be considered on a case-by-case basis, incorporating individual thrombotic and bleeding risks, recovery of ventricular function, and patient preferences through shared decision-
making.
Management of Right Heart Thrombi (RHT)
Right heart thrombi (RHT) are rare but potentially life-threatening findings, often associated with pulmonary embolism (PE) and right ventricular dysfunction. The management of RHT remains a clinical challenge due to the lack of randomized controlled trials and standardized treatment guidelines. However, observational studies and registry data suggest that anticoagulation alone is often insufficient, especially in cases involving mobile or serpiginous thrombi with high embolic potential.
Initial management typically includes systemic anticoagulation with intravenous unfractionated heparin or low molecular weight heparin. This serves as a bridge to definitive therapy and may be appropriate in hemodynamically stable patients with non-mobile thrombi or contraindications to more aggressive interventions.
For patients with mobile RHT or hemodynamic compromise, reperfusion strategies are generally preferred. Systemic thrombolysis has demonstrated lower mortality rates compared to anticoagulation alone, but carries a notable risk of major bleeding, including intracranial hemorrhage. Surgical embolectomy is another option, particularly in patients with contraindications to thrombolysis or when thrombi are large, organized, or entangled in cardiac structures.
Catheter-directed therapies, including percutaneous aspiration thrombectomy (e.g., AngioVac, FlowTriever, AlphaVac), have gained attention as minimally invasive alternatives. These techniques allow for rapid thrombus removal with high success rates and a lower bleeding profile compared to systemic thrombolysis. Early outcomes are promising, although data remain limited and long-term efficacy has not been firmly established.
Ultimately, the choice of therapy should be guided by thrombus characteristics
(size, mobility, morphology), patient stability, comorbidities, bleeding risk, and institutional expertise. In general, mobile RHTs or those associated with acute PE warrant urgent intervention beyond anticoagulation alone. Multidisciplinary decision making often involving cardiology, critical care, interventional radiology, and cardiothoracic surgery is essential for optimizing outcomes.
Prevention
Intracardiac thrombus formation is a recognized complication in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction, particularly in those with non-ischemic dilated
cardiomyopathy (DCM). Although left ventricular (LV) thrombi are more frequently documented, thrombi may also develop in the right heart chambers, especially in the presence of right-sided dysfunction, central venous catheters, cardiac devices, or systemic hypercoagulable states.
The use of antithrombotic therapy for primary prevention of thrombus formation in this population remains a subject of ongoing clinical judgment. In patients with DCM who are in sinus rhythm and without prior thromboembolic events, neither aspirin nor warfarin has consistently demonstrated clear benefit in preventing thrombus formation or reducing major adverse cardiovascular events. Therefore, routine prophylactic use of these agents is generally not recommended. However, individualized assessment is essential, especially when additional risk factors such as atrial fibrillation, prior embolic events, severely reduced ejection fraction, or left ventricular aneurysms are present.
In select subtypes of DCM that carry a higher inherent risk of intracardiac thrombus such as Takotsubo syndrome with apical ballooning, left ventricular
noncompaction, peripartum cardiomyopathy, eosinophilic myocarditis, and
infiltrative diseases like cardiac amyloidosis the use of oral anticoagulants (e.g.,
warfarin) or parenteral agents may be considered on a case-by-case basis. In
contrast, low-dose aspirin may offer some theoretical antiplatelet benefit, but its role in thrombus prevention remains less defined. Long-term anticoagulation may be appropriate for patients with persistent ventricular dysfunction or recurrent thromboembolic risk, provided the bleeding risk is acceptable.
Bibliografia link
Mathevosian, S., & Ranade, M. (2022). Right Heart Clot-in-Transit: Endovascular
Therapies. Seminars in interventional radiology, 39(5), 515–522.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-1757942
Sakellariou, X. M., Efstathopoulos, A., Stamatis, K. V., Nikas, D. N., & Kolettis, T.
M. (2020). Treatment of Mobile Right Heart Thrombi. European journal of case
reports in internal medicine, 7(12), 001918. https://doi.org/10.12890/2020_001918
Patel, A. N., Amrutiya, R. J., Manvar, B. N., & Patel, A. (2022). A proposed
approach for the management of clot-in-transit. Cureus, 14(8).
Lawrence LK Leung, M. D. (2025). Overview of hemostasis.
https://shorturl.at/hkxsH
Levine, G. N., McEvoy, J. W., Fang, J. C., Ibeh, C., McCarthy, C. P., Misra, A.,
Shah, Z. I., Shenoy, C., Spinler, S. A., Vallurupalli, S., Lip, G. Y. H., on behalf of
the American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on
Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, & and, S. C. (2022). Management of patients at
risk for and with left ventricular thrombus: A scientific statement from the american
heart association. Circulation, 146(15), e205–e223.
10.1161/CIR.0000000000001092
Warren J Manning, M. D. (2024). Echocardiography in detection of cardiac and
aortic sources of systemic embolism. https://shorturl.at/mR7gN
Watson, N. W., Weinberg, I., Dicks, A. B., Carroll, B. J., & Secemsky, E. A. (2024).
Clinical outcomes and predictors of advanced therapy for the management of right
heart thrombus. Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions, 17(4), e013637.
10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.123.013637
Wilson S Colucci, M. D., & Gregory YH Lip, MD, FRCPE, FESC, FACC. (2025).
Left ventricular thrombus. https://shorturl.at/Zf9oO
Kleindorfer, D. O., Towfighi, A., Chaturvedi, S., Cockroft, K. M., Gutierrez, J.,
Lombardi-Hill, D., Kamel, H., Kernan, W. N., Kittner, S. J., Leira, E. C., Lennon,
O., Meschia, J. F., Nguyen, T. N., Pollak, P. M., Santangeli, P., Sharrief, A. Z.,
Smith, S. C., Jr, Turan, T. N., & Williams, L. S. (2021). 2021 guideline for the
prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: A
guideline from the American heart association/American stroke association. Stroke;
a Journal of Cerebral Circulation, 52(7), e364–e467.
https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000375
Levine, G. N., McEvoy, J. W., Fang, J. C., Ibeh, C., McCarthy, C. P., Misra, A.,
Shah, Z. I., Shenoy, C., Spinler, S. A., Vallurupalli, S., Lip, G. Y. H., & American
Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Cardiovascular and
Stroke Nursing; and Stroke Council. (2022). Management of patients at risk for and
with left ventricular thrombus: A scientific statement from the American Heart
Association. Circulation, 146(15), e205–e223.
https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001092
Camaj, A., Fuster, V., Giustino, G., Bienstock, S. W., Sternheim, D., Mehran, R.,
Dangas, G. D., Kini, A., Sharma, S. K., Halperin, J., Dweck, M. R., & Goldman, M.
E. (2022). Left ventricular thrombus following acute myocardial infarction: JACC
state-of-the-art review. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 79(10),
1010–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2022.01.011
Sharma, N. D., McCullough, P. A., Philbin, E. F., & Weaver, W. D. (2000). Left
ventricular thrombus and subsequent thromboembolism in patients with severe
systolic dysfunction. Chest, 117(2), 314–320.
https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.117.2.314
Ram, P., Shah, M., Sirinvaravong, N., Lo, K. B., Patil, S., Patel, B., Tripathi, B.,
Garg, L., & Figueredo, V. (2018). Left ventricular thrombosis in acute anterior
myocardial infarction: Evaluation of hospital mortality, thromboembolism, and
bleeding. Clinical Cardiology, 41(10), 1289–1296. https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.23039
Albaeni, A., Chatila, K., Beydoun, H. A., Beydoun, M. A., Morsy, M., & Khalife,
W. I. (2020). In-hospital left ventricular thrombus following ST-elevation
myocardial infarction. International Journal of Cardiology, 299, 1–6.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.07.070